EchoScript for Map Mock
EchoScript is the core of Map Mock. It can work with both Map Local and Map Remote.
By default, EchoScript code is commented out, which means it does nothing.
// on_request := func(env, req) {// return {}// }
// on_response := func(env, res) {// return {}// }Callback functions
EchoScript has two standard callback functions: on_request and on_response, which can be used to modify HTTP(s) request and response respectively.
on_request
The return value of on_request is a map, which tells EchoProxy how to modify HTTP(s) request.
Return an empty map {} means it does nothing.
on_request := func(env, req) { return {}}The structure of on_request return value. All fields are optional.
{ // change request method, value can be GET/POST/PUT ... method: string, // change request URL url: string, // change request URL query parameters, merge with original map query: map, // change request header key/value pairs, merge with original map header: map, // change request cookie key/value pairs, merge with original map cookie: map, // change request body: a string, file, or map body: string|file|map}on_response
The return value of on_response is a map, which tells EchoProxy how to modify HTTP(s) response.
Return an empty map {} means it does nothing.
on_response := func(env, res) { return {}}The structure of on_response return value. All fields are optional.
{ // change response HTTP status code, value can be 200/302/404 ... code: int, // change response header key/value pairs, merge with original map header: map, // change response cookie key/value pairs, merge with original map cookie: map, // change response body: a string, file, or map body: string|file|map}Map modify strategy
When the field type is a map, the default modify strategy is to merge the two maps.
The other types (string|int|float|file|array) use assign strategy, which means the new value overwrite old value.
| field type | modify strategy |
|---|---|
map | merge |
string | assign overwrite |
int|float | assign overwrite |
file | assign overwrite |
array | assign overwrite |
Merge Example
Let’s take body field as an example. The original body value:
// callback function argument: req.body or res.body{ body: { "k1": 10, "k2": "hello", "k3": { "page": 3 }, "k4": [1, 2] }}The returned body value:
{ body: { "k2": "world", "k3": { "total": 50 }, "k4": [5, 6, 7] }}The final body value is the merge result of the two maps:
{ body: { "k1": 10, "k2": "world", "k3": { "page": 3, "total": 50 }, "k4": [5, 6, 7] }}Assign Example
The original body value is the same with previous example.
The returned body value is handled with function assign:
{ body: assign({ "k2": "world", "k3": { "total": 50 }, "k4": [5, 6, 7] })}The final body value will be the same with the assign argument:
{ body: { "k2": "world", "k3": { "total": 50 }, "k4": [5, 6, 7] }}Function arguments
req
The argument req represents the incoming HTTP request. The structure of req:
{ u: array, // holds Wildcard/Regex submatch strings url: string, // request URL method: string, // request method query: map, // request URL query parameters (string) header: map, // request header key/value pairs (string) cookie: map, // request cookie key/value pairs (string) body: string|map, // request body: a string or map text: string // request body as text string
client_ip: string, // client IP client_addr: string, // client address}on_request := func(env, req) { delete(req.query, "page") // modify req.query return { query: assign(req.query) // return with assign }}res
The argument res represents the response got from remote HTTP request (MapRemote),
or the response loaded from local file (MapLocal). The structure of res:
{ code: int, // response HTTP status code header: map, // response header key/value pairs (string) cookie: map, // response cookie key/value pairs (string) body: string|map, // response body: a string or map text: string // response body as text string}on_response := func(env, res) { delete(res.body, "name") // modify req.body res.body["msg"] = "updated!" // modify req.body return { body: assign(res.body) // return with assign }}env
The argument env is a map, which is designed to get and set enviroment variables.
TODO: under development
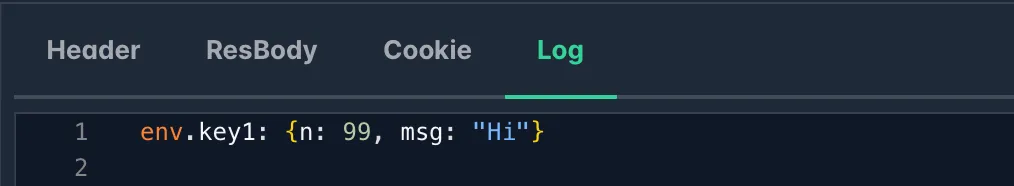
Example: Pass variable env.key1 from on_request to on_response, and print its value to Log tab.
on_request := func(env, req) { env["key1"] = { "n": 99, "msg": "Hi" } return {}}
on_response := func(env, res) { print("env.key1: ", env.key1) return {}}